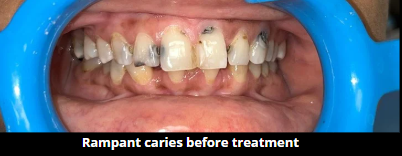
Despite advances in dental care, tooth decay remains a significant health issue among adults worldwide. This chronic disease, characterized by progressive destruction of tooth structure, affects nearly 28% of adults aged 20 to 64. Poor oral hygiene, frequent consumption of sugary foods and beverages, and inadequate access to dental care contribute to this widespread problem.
Recent studies indicate that the prevalence of untreated caries in adults has increased, particularly in socioeconomically disadvantaged populations. The consequences extend beyond oral health, impacting overall well-being, work productivity, and quality of life. Adults with untreated caries often experience chronic pain, difficulty eating, and decreased self-esteem.
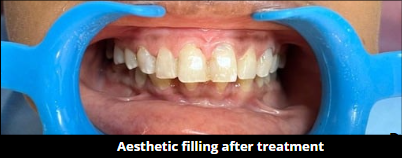
Prevention remains the most effective strategy, with experts recommending regular dental check-ups, proper brushing techniques, and dietary modifications. However, addressing the broader social determinants of oral health, including healthcare access and affordability, is crucial for reducing the burden of adult caries in our communities.